Media tools for visualising interactions in the city during COVID era 2020, United Kingdom, London
An agent-based simulation model that exploring the role of spatial configuration and human behaviour on the spread of the epidemic
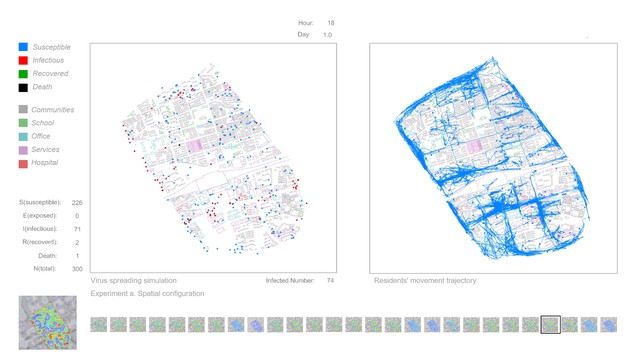
The COVID-19 epidemic in 2020 is a challenge facing all mankind. So far, a large number of infections have occurred during the virus spreading, which is accompanied by the interactions in the city related to the spatial configuration and public activities. This project explores how public space, defined through the configuration of the city, and human behaviour affect the spread of disease. In order to understand the virus spreading mechanism and influencing factors of the epidemic that accompanying residents movement, this project developed media tools to simulate interactions in the city in the COVID era using an agent-based simulation model. The case study is the city of Wuhan, China.
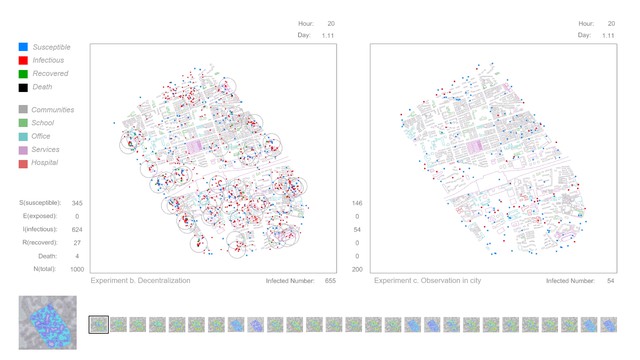
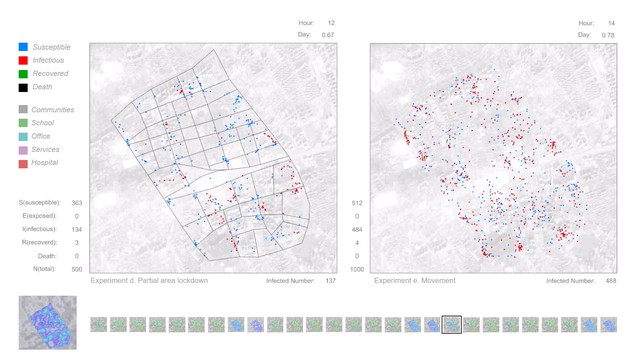
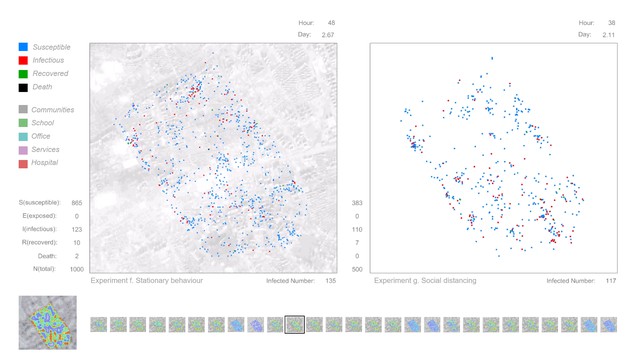
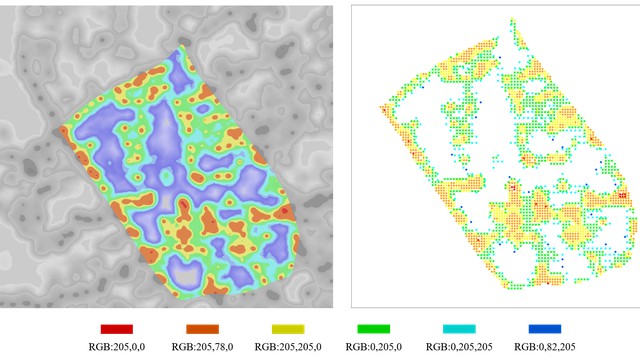
The simulation model can be divided into the movement model and the epidemic model. The Agent-based model can effectively simulate the behaviour of individuals. The movement model contains individual attributes and behaviour rules, which mainly driven by location data from the heat map(real location data based on residents which uploaded by mobile phone applications). Also, there are many other behaviours, Such as group, separate, observation and so on. In different city areas and public spaces, the behaviour rules and interaction mechanism of the agent can be set to make its movement behaviour occur autonomously in a predetermined framework. At the same time, this model also has a certain degree of randomness. In this project, the agent's actions are generally based on real data, which is convenient for studying the interactions between individual behaviour and city space. The epidemic model was constructed based on SIR(SEIR) compartmental models in epidemiology. And uses COVID-19 as a reference to set disease parameters. In the agent simulation process, each individual was given a state of the SIR(SEIR), and the virus spreading occurred during the movement and aggregation of different individuals and accompanied by the individual changes in the status of infectious diseases. In this way, to explore the spreading mechanism and influencing factors of the virus in the specific city area. After establishing the simulation model, start to simulate under different conditions. The first part of the experiments focuses on city space, which includes spatial configuration, Decentralization, Observation in the city, And partial area lockdown. These experiments are all focused on the interaction between the city and the individual; The second part of the experiments are focus on human behaviours, which include movement, stationary behaviour and social distancing. These experiments are all focused on the interaction between individuals. Finally, by analysing the simulation results of the agent's movement in the city area and the virus spreading under different conditions, the interactions in the city have been visualised, and the influence of factors of city configuration and human behaviour are explored.
Details
Team members : Mengda Wang
Supervisor : Associate Professor: Ava Fatah gen Schieck, Peters Koutsolampros
Institution : Bartlett School of Architecture, University college London
Descriptions
Technical Concept : The process can be briefly described as follows: a) First, select the public space and create the built environment required for simulation, which includes borders, obstacles (buildings) and other elements; b) Create an Agent-based model Simulation model, which can be divided into two parts: movement model an epidemic model. Among them, the movement model is mainly driven by residents' dynamic location data and gives individuals more behavioural capabilities; the epidemic model is built based on the mathematical models of SIR, which combines the real data of COVID-19. c) Simulation of the virus spreading, adjust some behaviour parameters and spatial parameters to simulate virus spreading under different conditions. The simulation software of this project is Rhino and Grasshopper, the programming language is C#, and some city spatial analysis uses Depth Map.
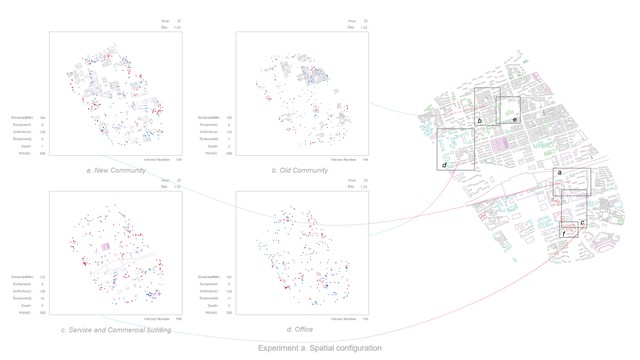
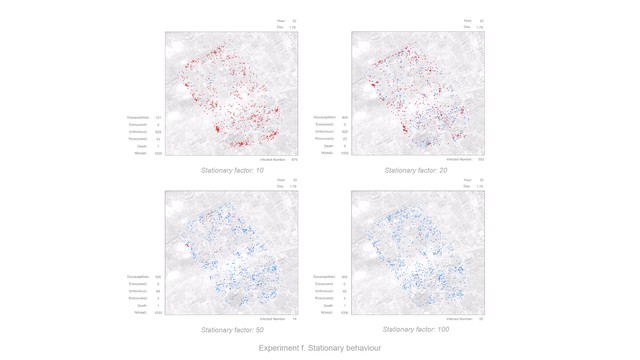
Visual Concept : The experiments show how public space(defined through the configuration of the city) and human behaviour affect the spread of virus. Simulation a to d focus on city space, and these experiments show the interaction between city and individual. (a) Spatial configuration: study the impact of spatial elements (shape, size, etc.) on virus spreading; (b) Decentralization: a strategy by setting up different numbers of city centres; (c) Observation in city: study the impact of vision on the extent of urban exploration; (d) Partial area lockdown: explore more possibilities of the lockdown strategy; Simulation e, f and g are focus on human behaviours. These experiments show the interaction between individuals. (e) Movement: explore individual moving speed; (f) Stationary behaviour: explore individual staying probability; (g) Social distancing: find effective distance in social activities.
Credits
Mengda Wang
Mengda Wang
Mengda Wang
Mengda Wang
Mengda Wang
Mengda Wang
Mengda Wang
Mengda Wang
Mengda Wang